I recently returned to southern Ontario from a novel-research trip to the Arctic, where I hope next time to see the incredible northern lights (this recent visit was during their midnight sun period; so, no luck with northern lights). But, in the future I may not have to travel north to see them…
My eco-novel A Diary in the Age of Water begins sometime in the future with Kyo, a blue multi-armed being, living in the dying boreal forest of post-apocalypse Canada; Kyo finds a diary by Lynna Dresden, a limnologist from the calamitous time when climate change ravaged the planet and when the Water Twins destroyed humanity. Yearning for clarity about that holocaust, Kyo reads the diary.
Lynna begins her February 24, 2057 diary entry with a definition of the Aurora Borealis:
“Also called northern lights, this is a natural electrical phenomenon caused by the interaction of electrically charged particles from the sun with the upper atmosphere near the north magnetic pole. It is characterized by the appearance of bands of reddish, greenish, and other coloured lights in the sky that follow the magnetic lines of force. The colours differ based on the type of gas particles that are colliding. The most common colour—a pale yellowish-green—comes from oxygen molecules some sixty miles above the earth. All-red auroras are rare and are associated with high-altitude oxygen, up to two hundred miles high. Nitrogen produces blue or purplish-red aurora.”
Lynna lives with her daughter Hilde in now warm Toronto, in southern Canada, where the northern lights had been up to recently only rarely observed. By 2057, this has changed:
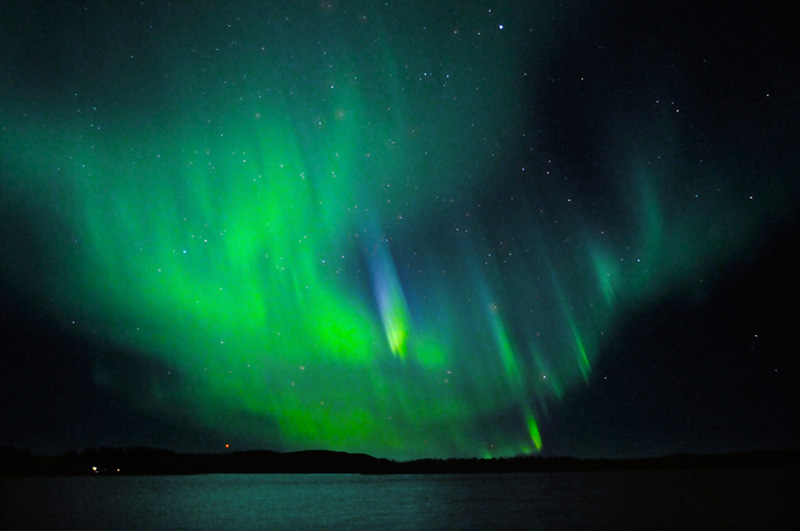
Last night after supper, Hilde and I went for a walk along Shaw to Christie Pits, where I used to play as a kid. She wanted to show me the magnificent aurora borealis that had been streaming dramatically for the past several weeks. When I was a kid, auroras this far south were unheard of. Now they are common. The night sky was clear, and we enjoyed the fresh spring air as we ambled down Shaw Street. We parked ourselves on the damp grass among other spectators of the colourful night sky and watched the dancing light show. It was mesmerizing: ribbons of mostly green and pink light rippled as if tugged by a mischievous wind. They danced with a kind of life that brought me back to my childhood.
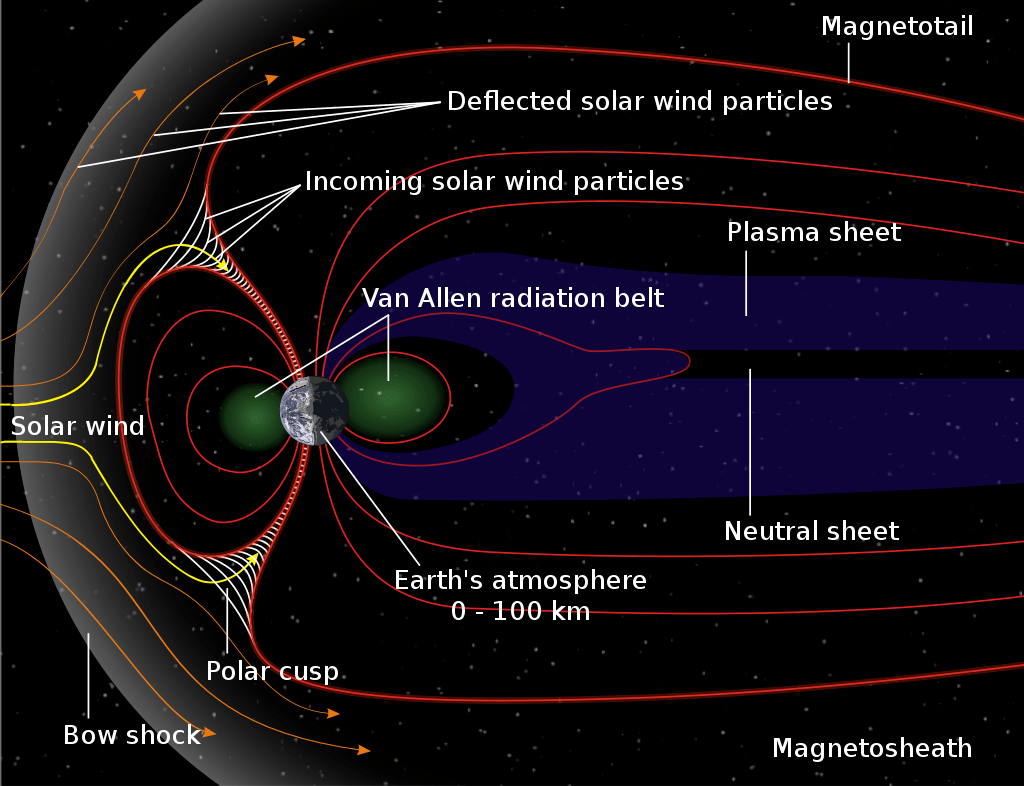
Northern lights happen when the magnetic field of our planet is disturbed by the solar wind. As the particles slide along the contours of the Earth’s magnetosphere, they glow as they lose their energy. The particles energize the air molecules enough to make them glow in various colours, depending on the composition of the gases.
Earth’s magnetic field is generated and maintained by an ocean of superheated, swirling metal around a solid iron core. These act like a dynamo to create electrical currents, which, in turn, create our magnetic field. But our magnetic field is weakening, and a flip is imminent. In the past two hundred years, the field has weakened by fifteen percent. That’s why we’re seeing these auroras in Toronto. A weaker field creates more auroras. They’ve become common here, particularly during the winter and spring months. NASA predicts that the field could be gone in five hundred years or less and then take another two hundred years to rebuild.
The field will first become more complex and might show more than two magnetic poles—playing havoc with our navigation systems and God knows what else—until it is entirely gone. Then it will presumably build and align in the opposite direction. When the magnetic field goes, so will our shield against radiation. First, the ozone layer—our shield against ultraviolet rays—will be stripped away, and then the atmosphere may lose other key elements and grow thinner. Will we end up like Mars 4.2 billion years ago, when severe solar storms stole its very atmosphere and evaporated all its water?
Mars once had a strong magnetic field like Earth. But then Mars cooled and its conducting geodynamo stopped rotating. In the absence of the protective field, the solar wind surged in and excited the ions in the upper Martian atmosphere to an escape velocity. The solar wind just swept the air away. The surface pressure of the Martian atmosphere dwindled from one thousand millibars to six millibars. Mars lost about the same atmosphere that Earth has today.
Mars is our destiny; it’s just a question of when. We’re all batteries, running dry. I considered this probable fate for Earth as we watched the exquisite example of our changing magnetic field. But I didn’t share it with Hilde, who watched with her mouth open in rapt wonder. If she’s lucky, she will experience no more of this progression than these amazing auroras. The weakening magnetic field and the associated loss of protection and atmosphere won’t happen for a while. I hope.
I shared none of my thoughts with Hilde.”
A Diary in the Age of Water
How Auroras Work
The Aurora Borealis is named after the Roman goddess of the dawn, Aurora, and the Greek name for north wind, Boreas. According to scientists, the colourful and eerie streams of light known as the Aurora Borealis result from “magnetic ropes” that link the Earth’s upper atmosphere to the sun. Solar winds surf them, providing energy for geomagnetic storms and auroras. NASA researchers describe the “ropes” as “a twisted bundle of magnetic fields organized much like the twisted hemp of a mariner’s rope.”
The earth is constantly immersed in the solar wind, a rarefied flow of hot plasma emitted by the sun in all directions. Auroras happen when charged particles from the magnetosphere collide with atoms and molecules of the Earth’s upper atmosphere (at altitudes above 80 km). Most of these particles originate from the sun and arrive in a relatively low-energy solar wind. When the trapped magnetic field of the solar wind is favourably oriented (mostly southwards) it reconnects with the earth’s magnetic field and solar particles then enter the magnetosphere and are swept to the magnetotail. Further magnetic reconnection accelerates the particles towards earth.
These atmospheric collisions electronically excite atoms and molecules in the upper atmosphere. The excitation energy can be lost by light emission or collisions. Most auroras are green and red emissions from atomic oxygen. Molecular nitrogen and nitrogen ions produce some low level red and very high blue/violet auroras. Typically, an aurora appears either as a diffuse glow or as “curtains” that extend more or less in an east-west direction. Each curtain is made of many parallel rays, each lined up with the local direction of the magnetic field lines, suggesting that aurora are shaped by the earth’s magnetic field.
The earth’s magnetosphere is the space region dominated by its magnetic field. It forms an obstacle in the path of the solar wind, causing it to be diverted around. When the solar wind is “perturbed”, it transfers energy and material into the magnetosphere. The electrons and ions in the magnetosphere that become energized move along the magnetic field lines to the polar regions of the atmosphere.
Auroras have been observed on Jupiter, Saturn, Venus, Mars, Uranus and Neptune. The auroras on the gas giants appear to be powered by the solar wind. In addition, Jupiter’s moons, especially Io, are powerful sources of auroras. These come from electric currents along field lines, generated by a dynamo mechanism due to the relative motion between the rotating planet and the moving moon. Io, which experiences active volcanism and has an ionosphere, is a particularly strong source, and its currents also generate radio emissions.
The passage I quoted from A Diary in the Age of Water was based on current science by NASA and real predictions by scientists. It isn’t so much a question of what, but of when… Who will witness the change in the magnetic pole?


Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press (Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” was released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.